Understanding Pneumonia: Your Guide
Pneumonia is a common respiratory infection that can range from mild to severe, affecting people of all ages. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection, proper treatment, and prevention. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of pneumonia, from its causes and symptoms to treatment options and prevention strategies.
Introduction to Pneumonia
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Types of pneumonia
There are several types of pneumonia, classified based on the causative agent:
- Bacterial pneumonia: Caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Viral pneumonia: Caused by viruses such as influenza or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- Fungal pneumonia: Caused by fungi like Pneumocystis jirovecii.
Importance of understanding pneumonia
Understanding pneumonia is crucial as it helps individuals recognize its symptoms early on, seek prompt medical attention, and adopt preventive measures to reduce the risk of infection.
Causes and Risk Factors
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae but can also result from other bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae or Staphylococcus aureus.
Viral pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is commonly caused by influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), or the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19.
Fungal pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is less common and usually affects individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or individuals undergoing chemotherapy.
Risk factors for developing pneumonia
Several factors can increase the risk of developing pneumonia, including age (young children and the elderly are more vulnerable), weakened immune system, chronic diseases (such as COPD or diabetes), smoking, and exposure to pollutants or environmental toxins.
Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia may vary depending on the causative agent but often include:
- Fever and chills
- Cough, often with phlegm
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Fatigue and weakness
Complications of pneumonia
In severe cases, pneumonia can lead to complications such as respiratory failure, sepsis, or lung abscess.
When to seek medical help
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of pneumonia, especially if you belong to high-risk groups or if symptoms worsen over time.
Diagnosis
Physical examination
During a physical examination, your healthcare provider will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for abnormal breath sounds.
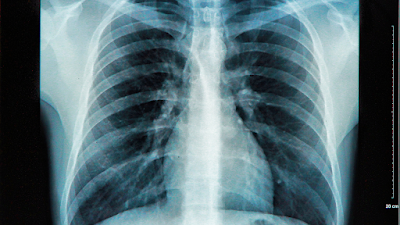
Imaging tests
Imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis of pneumonia and assess its severity.
Laboratory tests
Laboratory tests, including blood tests and sputum cultures, may be performed to identify the causative agent of pneumonia.
Treatment Options
Antibiotics
Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications.
Antiviral medication
Antiviral medications such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) may be prescribed for viral pneumonia caused by influenza viruses.
Supportive care
Supportive care measures such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications for fever and pain relief can help alleviate symptoms of pneumonia.
Prevention
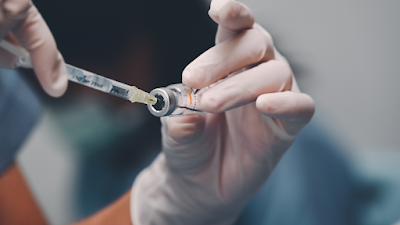
Vaccination
Vaccination against common pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza can help prevent pneumonia.
Good hygiene practices
Practicing good hand hygiene, covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can help reduce the risk of pneumonia transmission.
Avoiding smoking and pollutants
Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to pollutants or environmental toxins can help protect against respiratory infections, including pneumonia.
Living with Pneumonia
Recovery process
Most people recover from pneumonia with proper treatment and rest, although it may take several weeks to fully regain strength.
Lifestyle adjustments
Making lifestyle adjustments such as getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and eating a healthy diet can aid in the recovery process.
Follow-up care
Follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider may be necessary to monitor your recovery and ensure that pneumonia has resolved completely.
Pneumonia in Specific Groups
Pneumonia in children
Pneumonia is a leading cause of death in children worldwide, but timely vaccination and access to healthcare can help prevent and treat childhood pneumonia effectively.
Pneumonia in the elderly
Older adults are at increased risk of developing pneumonia due to age-related changes in the immune system and underlying health conditions.
Pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to pneumonia and may require specialized treatment.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Respiratory complications
Pneumonia can lead to respiratory complications such as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) or pleural effusion.
Risk of recurrence
Some individuals may experience recurrent episodes of pneumonia, especially if they have underlying lung conditions or weakened immune systems.
Chronic conditions associated with pneumonia
In some cases, pneumonia can lead to chronic health problems such as bronchiectasis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
FAQs
What are the main symptoms of pneumonia?
- The main symptoms of pneumonia include fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and weakness.
Can pneumonia be prevented?
- Pneumonia can be prevented through vaccination, practicing good hygiene, avoiding smoking, and minimizing exposure to pollutants.
How long does it take to recover from pneumonia?
- Recovery from pneumonia varies depending on the severity of the infection and individual health factors but may take several weeks.
Is pneumonia contagious?
- Yes, pneumonia can be contagious, especially if caused by bacteria or viruses. It is important to practice good respiratory hygiene to prevent transmission.
Can pneumonia lead to other health problems?
- Yes, pneumonia can lead to complications such as respiratory failure, sepsis, or long-term respiratory issues in some cases.
In conclusion, understanding pneumonia is essential for maintaining respiratory health and preventing serious complications. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of pneumonia, seeking prompt medical attention, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of infection and protect their overall well-being.